Go 源码之 gorm 框架
目录
看源码先看底层核心数据结构
整体核心流程
open方法的核心流程
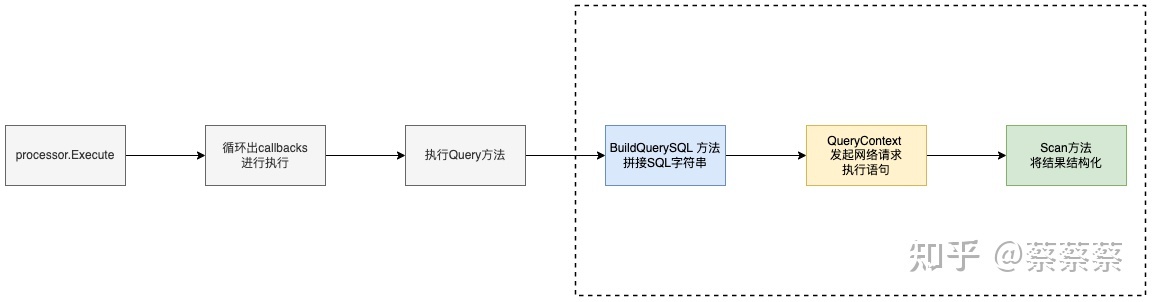
完整的sql执行过程
// db.Table(tableName).Create(model)// var tx=db.Table(tableName)
// tx.callbacks.Create().Execute(tx)
// tx.callbacks ---> 钩子函数,open()内会调用Initialize()函数,注册gorm的操作sql的api如update,create,save等默认的钩子函数结构 *processor
// tx.callbacks.Create() 取到 create类型的*processor
// Execute(tx) 执行具体类型(如create类型的*processor)的钩子函数,具体的sql执行在钩子函数create中并发安全模型
gorm 处理并发冲突的方法和 golang 的 context 相似,通过复制 db 结构解决;具体详见 clone的设计
Statement的生成
func (db *DB) Where(query interface{}, args ...interface{}) (tx *DB) {
// 此处复制一个DB实例
tx = db.getInstance()
// 将对应的条件进行构造并加入到Statement结构中,将 类似id = ? 等条件进行转化 , 构造出 clause.Expression对象
if conds := tx.Statement.BuildCondition(query, args...); len(conds) > 0 {
tx.Statement.AddClause(clause.Where{Exprs: conds})
}
return
}
func (db *DB) getInstance() *DB {
// 单例模型,Clone 出来后不再进行重复clone
if db.clone > 0 {
tx := &DB{Config: db.Config, Error: db.Error}
// 第一次Clone则直接将Statement的语句进行构造,否则对Statement 进行复制即可
if db.clone == 1 {
// clone with new statement
tx.Statement = &Statement{
DB: tx,
ConnPool: db.Statement.ConnPool,
Context: db.Statement.Context,
Clauses: map[string]clause.Clause{},
Vars: make([]interface{}, 0, 8),
}
} else {
// with clone statement
tx.Statement = db.Statement.clone()
tx.Statement.DB = tx
}
return tx
}
return db
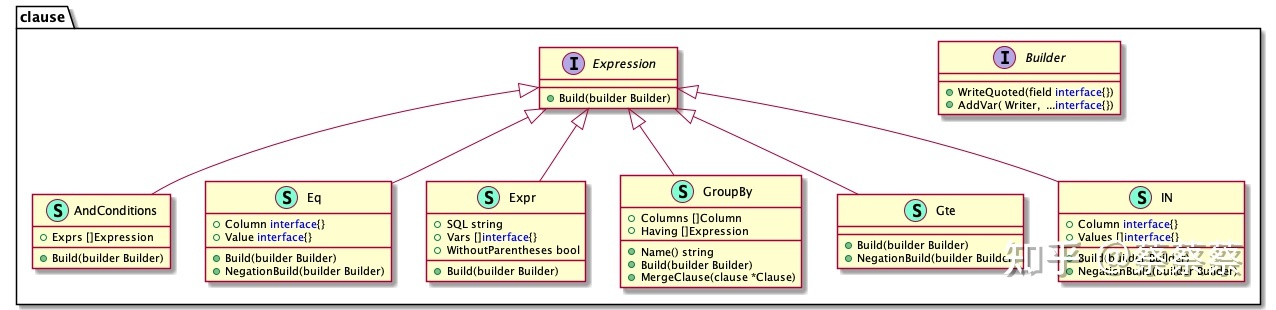
}clause.Expression 为Interface ,SQL 各种表达通过实现Build方法来生成对应字符串。 以下为对应的部分UML图:
执行流程
callbacks 包下面包含全部gorm 自带的方法,以查询方法为例进行讲解构建SQL:
func RegisterDefaultCallbacks(db *gorm.DB, config *Config) { queryCallback := db.Callback().Query()
// 注册相应的查询方法
queryCallback := db.Callback().Query()
queryCallback.Register("gorm:query", Query)
queryCallback.Register("gorm:preload", Preload)
queryCallback.Register("gorm:after_query", AfterQuery)
queryCallback.Clauses = config.QueryClauses
}
func Query(db *gorm.DB) {
if db.Error == nil {
// 1.构建查询的SQL
BuildQuerySQL(db)
// 2.真正对语句进行执行,并返回对应的Rows结果
if !db.DryRun && db.Error == nil {
rows, err := db.Statement.ConnPool.QueryContext(db.Statement.Context, db.Statement.SQL.String(), db.Statement.Vars...)
gorm.Scan(rows, db, 0)
}
}
}
func BuildQuerySQL(db *gorm.DB) {
// 核心构建语句,通过Build 拼接出对应的字符串
db.Statement.Build(db.Statement.BuildClauses...)
}底层数据结构
DB(超级核心结构)
// DB GORM DB definition
type DB struct {
*Config
Error error
RowsAffected int64
// Statement 存储的所有sql条件,最后会build为完整的sql
Statement *Statement
// clone的设计就非常的巧妙了;clone一共有三种值
// 详见 【gorm的clone的设计】
// https://www.zhihu.com/question/430806549
clone int
}Statement(DB内嵌结构)
// Statement statement
type Statement struct {
*DB
TableExpr *clause.Expr
Table string // 表名,通过db.Table()设置
Model interface{} // 模型,通过db.Model()设置
Unscoped bool
Dest interface{} // 响应数据回写结构
ReflectValue reflect.Value
Clauses map[string]clause.Clause
BuildClauses []string
Distinct bool
Selects []string // selected columns
Omits []string // omit columns
Joins []join
Preloads map[string][]interface{}
Settings sync.Map
ConnPool ConnPool
Schema *schema.Schema
Context context.Context
RaiseErrorOnNotFound bool
SkipHooks bool
SQL strings.Builder
Vars []interface{}
CurDestIndex int
attrs []interface{}
assigns []interface{}
scopes []func(*DB) *DB
}Chain Method
比如Where、Limit、Select、Tables、Join、Clauses等等,这些在语句执行被执行前,设置和修改语句内容的,都叫 Chain Method
Finisher Method
比如Create、First、Find、Take、Save、Update``Delete、Scan、Row、Rows等等,会设置和修改语句内容,并执行语句的,都叫 Finisher Method。
New Session Method
比如Session、WithContext、Debug 这三个方法,他们会新建一个Session。WithContext和Debug 都只是Session方法特定调用的简写,底层都是调用的Session方法。
Statement
每个*gorm.DB 实例都会有一个Statement的字段,Statement就是我们真正要执行的语句,我们的 Chain Method 和 Finisher Method,事实上都是在修改Statement这个结构体。最后这个结构体会被渲染为SQL语句。
Config
// Config GORM config
type Config struct {
// GORM perform single create, update, delete operations in transactions by default to ensure database data integrity.You can disable it by setting `SkipDefaultTransaction` to true
// 为了确保数据一致性,GORM 会在事务里执行写入操作(创建、更新、删除)。如果没有这方面的要求,您可以在初始化时禁用它。
// 系统的默认事务:我们的gorm连接到数据库后,我们所做的增删改查操作,只要是这种链式的,gorm会自动的帮我们以事务的方式给串联起来,保证数据的一致性
SkipDefaultTransaction bool
// NamingStrategy tables, columns naming strategy
// 表名命名策略,在使用AutoMigter时,会将model的名转小写并+s,SingularTable: true, // love表将是love,不再是loves,即可成功取消表明被加s,或者在model结构实现TableName()方法即可自定义表名
NamingStrategy schema.Namer
// FullSaveAssociations full save associations
// 在创建、更新记录时,GORM 会通过 Upsert 自动保存关联及其引用记录
FullSaveAssociations bool
// Logger 支持自定义logger实现
Logger logger.Interface
// NowFunc the function to be used when creating a new timestamp
// 更改创建时间使用的函数
NowFunc func() time.Time
// DryRun generate sql without execute
// 生成 SQL 但不执行,可以用于准备或测试生成的 SQL,参考 会话 获取详情
DryRun bool
// PrepareStmt executes the given query in cached statement
// PreparedStmt 在执行任何 SQL 时都会创建一个 prepared statement 并将其缓存,以提高后续的效率,参考 会话 获取详情
PrepareStmt bool
// DisableAutomaticPing
// 在完成初始化后,GORM 会自动 ping 数据库以检查数据库的可用性,若要禁用该特性,可将其设置为 true
DisableAutomaticPing bool
// DisableForeignKeyConstraintWhenMigrating
DisableForeignKeyConstraintWhenMigrating bool
// DisableNestedTransaction disable nested transaction
// 禁用嵌套事务;GORM 会使用 SavePoint(savedPointName),RollbackTo(savedPointName) 为你提供嵌套事务支持
DisableNestedTransaction bool
// AllowGlobalUpdate allow global update
AllowGlobalUpdate bool
// QueryFields executes the SQL query with all fields of the table
// 默认select * from,QueryFields=true的情况下,
QueryFields bool
// CreateBatchSize default create batch size
// 设置批量创建的最大数
CreateBatchSize int
// ClauseBuilders clause builder
ClauseBuilders map[string]clause.ClauseBuilder
// ConnPool db conn pool
ConnPool ConnPool
// Dialector database dialector
Dialector
// Plugins registered plugins
Plugins map[string]Plugin
// 回调函数,又称钩子函数
callbacks *callbacks
cacheStore *sync.Map
}Session(TODO)
// Session session config when create session with Session() method
// Seesion用来重新配置DB结构中的Config结构的
type Session struct {
DryRun bool
PrepareStmt bool
NewDB bool
SkipHooks bool
SkipDefaultTransaction bool
DisableNestedTransaction bool
AllowGlobalUpdate bool
FullSaveAssociations bool
QueryFields bool
Context context.Context
Logger logger.Interface
NowFunc func() time.Time
CreateBatchSize int
}Context(TODO)
Processor
// 最终的sql处理器:1.model的处理;2.回写数据结构dest的处理;3.
type processor struct {
db *DB
Clauses []string
fns []func(*DB) // 将callbacks排序后的钩子函数
callbacks []*callback // 钩子函数
}
// 核心处理方法,基本上所有的操作最终都会走这个方法,注意,该方法内部没有具体的执行sql的代码,原因是该方法只会执行 钩子函数,
// 而gorm的操作sql的api如update,create,save等都是在初始化(Initialize)的时候默认注册了钩子函数
func (p *processor) Execute(db *DB) *DB {}源码
钩子函数的设计
// 默认的钩子函数,如query,create,update,delete等
open()-->Initialize(db *gorm.DB)-->callbacks.RegisterDefaultCallbacks()-->callback.Register()
callback.Register():callback是*processor结构,表示指定类型(如create)处理器,Register()内部调用compile()会注册钩子函数到 *processor结构中的fns数组(最后执行的数据一次执行)
compile() 函数将注册的钩子函数进行排序操作,按照 before 还是after 添加在fns数组中默认钩子函数的前还说后
如:
// 我们手动注册一个 create的前置钩子函数,大概的流程为:open()执行后,db.fns数组中会存在一个默认的Create函数,前置钩子函数handler1会注册到fns数组的默认Create函数之前,fns变为[handler1,Create]
db.Callback().Create().Before("gorm:create").Register("gorm:auto_migrate", handler1)
// 后置钩子函数handler2会注册到fns数组的默认Create函数之后,fns变为[handler1,Create,handler2]
db.Callback().Create().After("gorm:create").Register("gorm:auto_migrate", handler2)
最终在*processor.Execute()方法中会遍历执行fns数组,从而达到拦截器(中间件)的作用Statement的设计
open函数
func Open(dialector Dialector, opts ...Option) (db *DB, err error) {
// 1.初始化配置,通过opts 来设置可变参数
config := &Config{}
// 2.配置进行应用
if d, ok := dialector.(interface{ Apply(*Config) error }); ok {
if err = d.Apply(config); err != nil {
return
}
}
// 3.初始化gorm.DB对象,后续操作通过clone 该对象进行调用
db = &DB{Config: config, clone: 1}
// 初始化执行函数
db.callbacks = initializeCallbacks(db)
// 4.通过Initialize方法建立连接
if dialector != nil {
config.Dialector = dialector
}
if config.Dialector != nil {
err = config.Dialector.Initialize(db)
}
return
}
// 初始化执行函数
func initializeCallbacks(db *DB) *callbacks {
return &callbacks{
processors: map[string]*processor{
"create": {db: db},
"query": {db: db},
"update": {db: db},
"delete": {db: db},
"row": {db: db},
"raw": {db: db},
},
}
}Initialize 方法通过调用databases.sql 的 connect 建立起对数据库的连接。最终建立的连接会通过driverConn 结构体进行保存